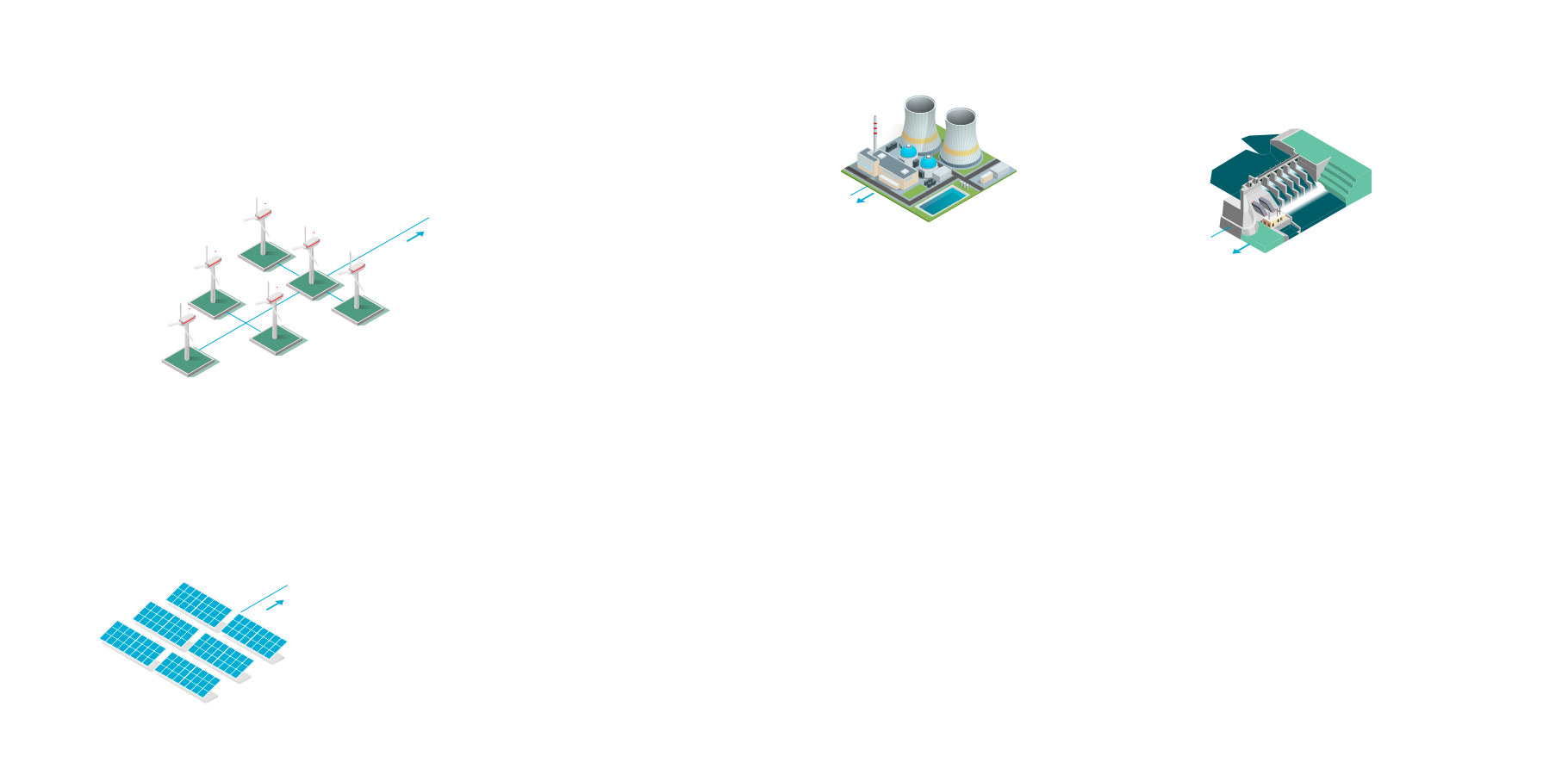
Solar power station

Generates electricity from solar energy. Performance depending on day/night time and weather conditions.

Windpark

Generates electricity from wind power. Performance depends on weather conditions and ranges from 1.5 to 8 MW per wind generator

Thermal power plant

Generates electricity from the steam that turns a turbine. Steam is produced from heating water with fossil energy, e.g. coal.

Hydro power plant
Generates electricity from a rotating turbine that is driven by water flows. Are often used to balance load peaks when there is a high energy demand.

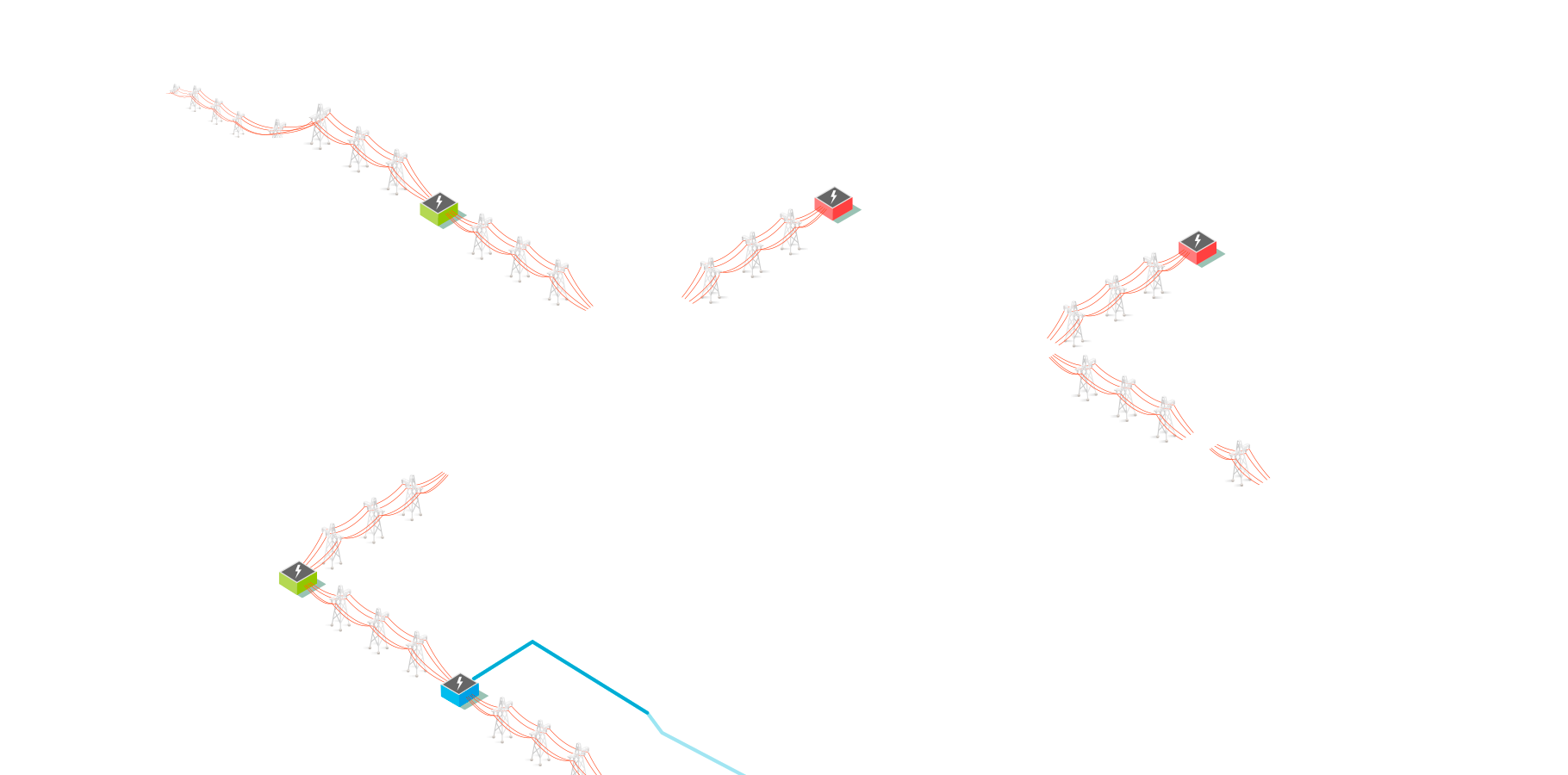
Collector substation

Transforms renewable power from medium voltage to transmission voltage.
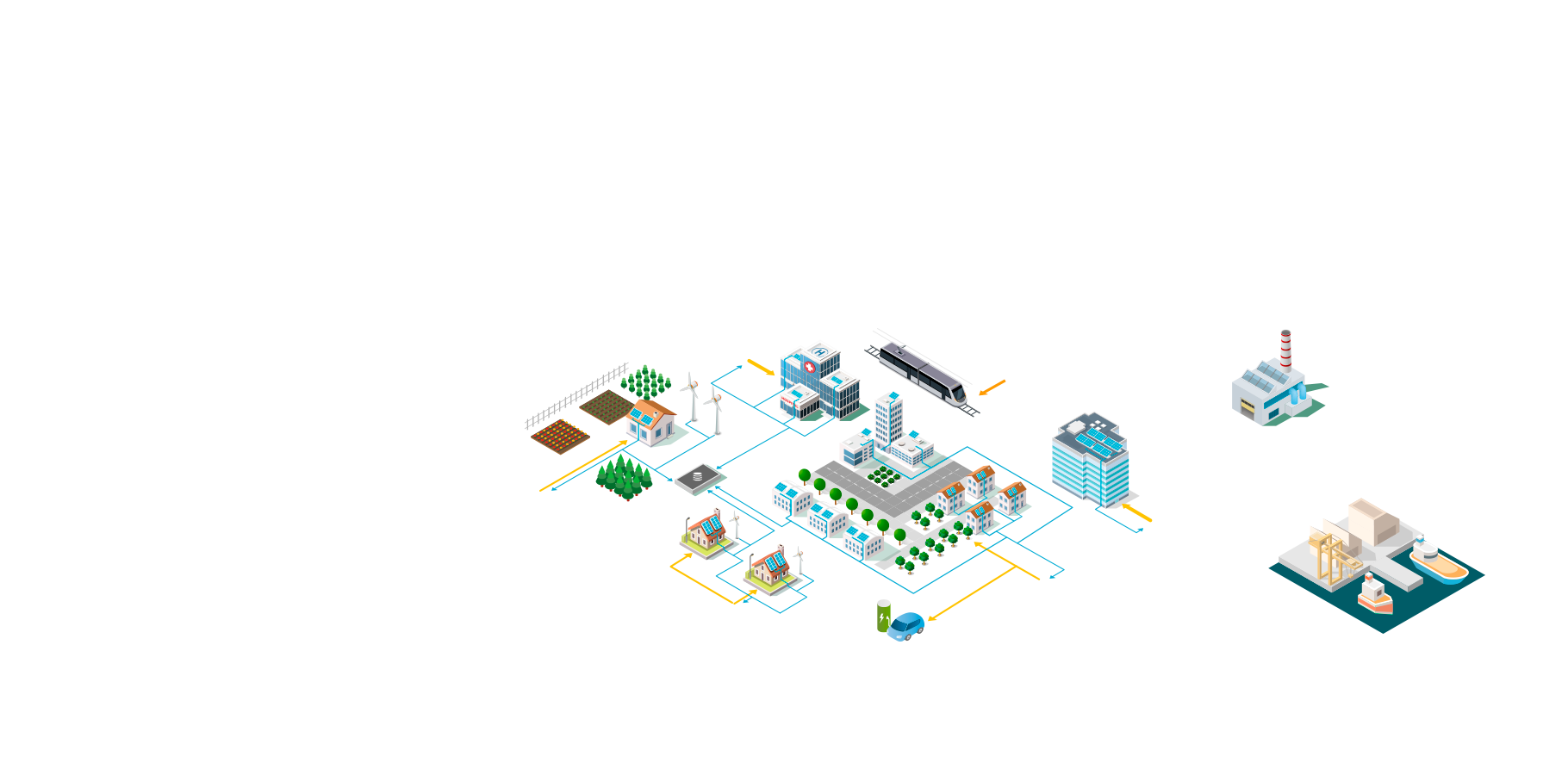
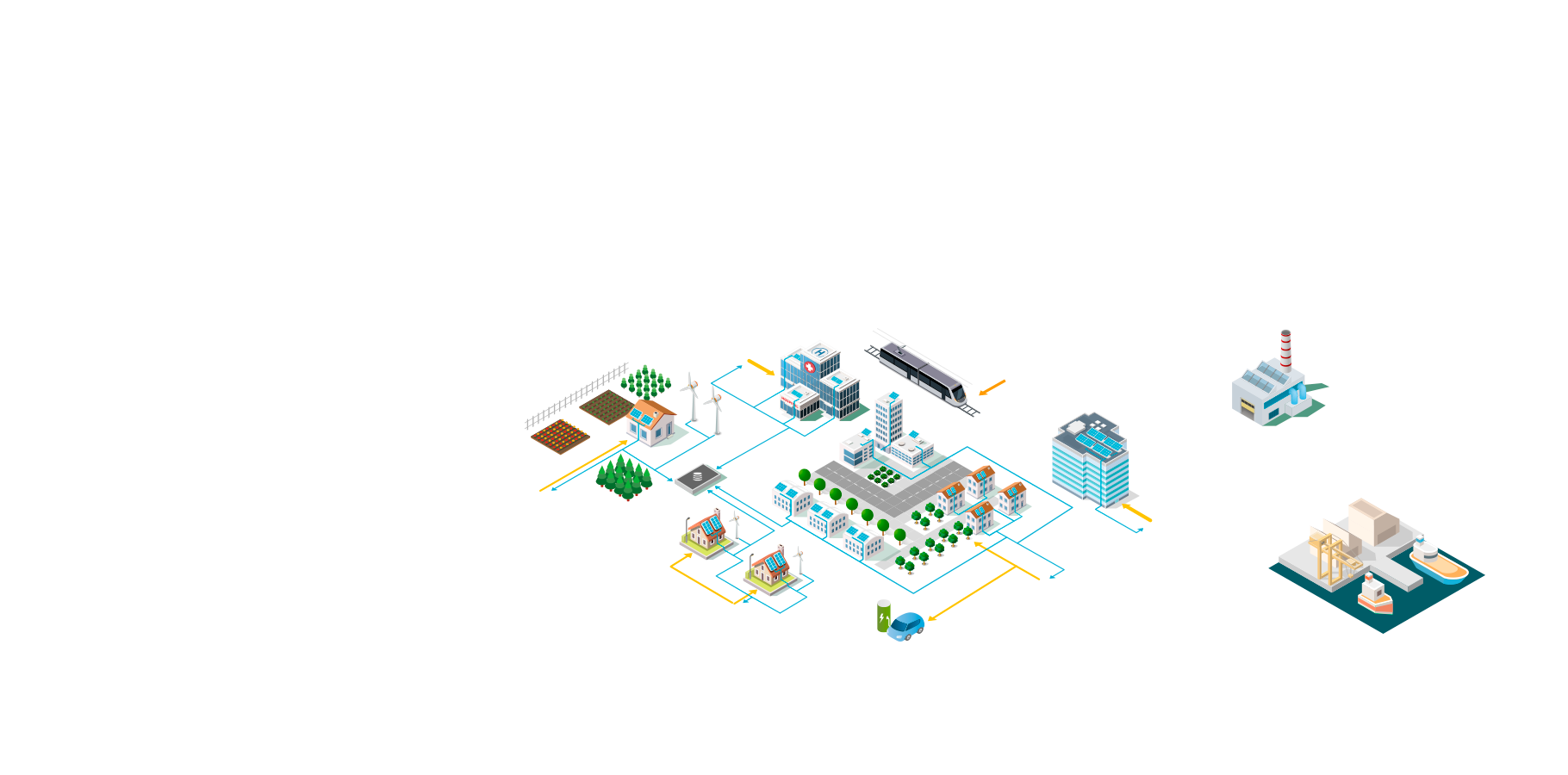
Distribution network

Regional distribution of electrical energy
Industrial users

Big industrial consumers (e.g. Aluminium smelters, cement companies). Needs high voltage power supply

Port electrification

Shore-side electricity allows ships to be powered without using their diesel engine when docked. CO2 and noxious gas emissions are prevented.

Railway infrastructure

Specific and separate electricity grid with individual AC frequency or DC supply to provide power to trains

Hospital / critical infrastructure

Need for particularly reliable power supply, often double secured with diesel standby emergency generators.

Urban area

Concentrates multiple electricity consumers on a limited space. Distributed energy resources are developing in cities with solar panels on buildings.

Rural area

Distributed energy such as solar panels on roofs and windmills are providing rural prosumers with clean power.

Grid storage

Energy produced by renewables can be stored using different methods (batteries, compressed air, water) and used when the grid needs it.

Primary substation

Transforms power from a transmission voltage to a distribution voltage.
Large switching substation MV/MV
A substation which includes switchgear and usually bussbars, but no power transformers.
Secondary substation MV/LV

Transforms power from medium voltage to low voltage.
Generator transformer station

Transforms power from medium voltage to transmission voltage.
Transmission network

Upper level of electricity provision. Transports electrical energy over long distances, both nationally and cross-border.


Converter for HVDC submarine transmission

Transforms medium voltage to transmission voltage (AC to DC) power.

Power charging station for EV

Electric mobility needs a reliable power charging infrastructure connected to the distribution network.